Data Warehouse Architecture
Understanding Data Warehouse Architecture
Introduction
Data is the lifeblood of any modern business, and as data volume and complexity grow, so does the need for efficient, scalable data management solutions. This is where a well-architected data warehouse comes into play. In this article, I’m going to break down the key components of a data warehouse architecture, including how data flows from raw sources through ETL processes, into structured presentation areas, and ultimately powers business intelligence applications.
Architecture
Data warehouse architecture consists of 4 components:
- Source Systems
- ETL Layer
- Enterprise Data warehouse
- BI/Presentation Layer
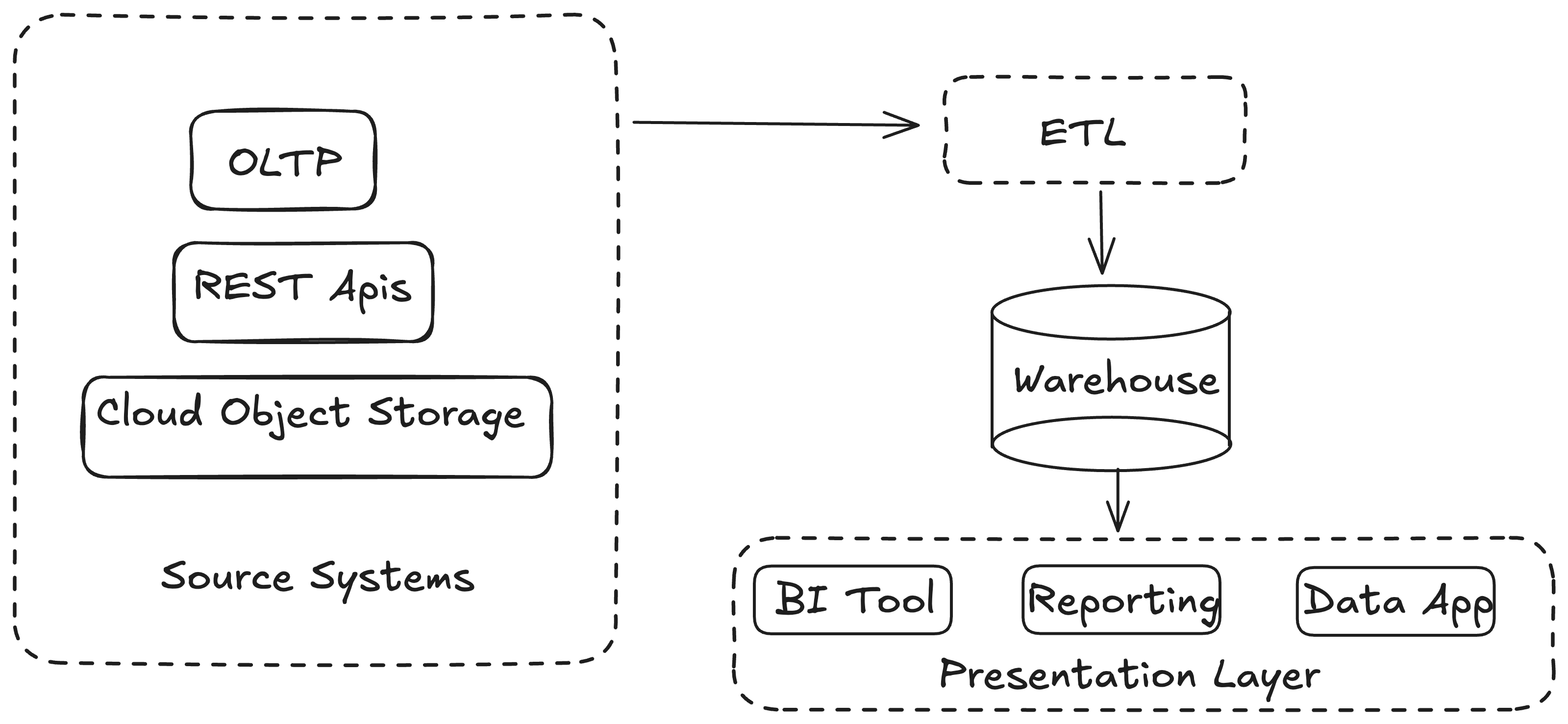
I am going to provide details on all of these above components in more details which will give you more clarity.
Source System
Source systems are the system which are producing the data. Data warehouse depending on the business processes, should accomodate various type of data. Let me provide you a simple example to better understand it.
Let us assume you are owner of a consulting firm. In the consulting firm, you are using various SAAS/tools/excel to track various business operations which includes sales, time tracking, HR activities, accounting etc. For the management and business team to take into account various aspects of the business, all these data sources must be placed togather in such a way that it becomes easy for analyst/management to investigate data and drive data backed initialtives. This is where data warehouse comes into the picture. It hold all the relevant and important imformation an organization needs to take data driven decisions and adapt to ever changing business scenarios.
ETL
ETL stands for extract, transform and load. As I mentioned in the above section, data warehouse typically hold various data sources. These sources can be another database, datawarehouse, rest api, cloud storage, excel/csv data dumps etc. ETL layer is responsible for extracting the data from the source, perform the necessary transformations and then load the data in the datawarehouse.
ETL layer also takes care of the duplicate data, null data and other skewed data based on the use case. In ideal case scenario, ETL layer will make sure that all the quality data lands in the datawarehouse. There are many tools and technologies which are being used to perform ETL. ETL itself is a huge part of the overall data eco-system.
Enterprise Data Warehouse
This is the actual place where data is stored and being used by various teams for analysis. Traditionally data warehouses used to be very expensive to setup on-premises and maintain. A huge set of professionals were required to create and maintain a datawarehouse. After the introduction of the cloud based data warehouse, it became relative easy to setup and use data warehouse. Pay-as-you-go model allowed smaller teams and companies to adopt data warehouse and become more data driven.
Presentation Layer
This layer is responsible for building reporting, dashboards or data apps using the data warehouse. Typically these applications are used by the management or the business users. Data analysts/data scientists slice and dice through the data and make reports/dashboards available for the end users.
What next?
We are just stratching the surface and I am trying to make it very simple at these stage. As we learn more around this topic, you will get a better idea on how and where exactly data warehouse is utilized. Stay tuned for the upcoming posts.

Twitter
Reddit
LinkedIn
Pinterest
Email